How Long Til My Paphedelium Blooms Again





Strawberry plants are a wonderful forb. Their life cycle is much more complicated than the elementary advent of the humble strawberry plant implies. The growth bicycle of strawberry plants spans the entire year and repeats annually. The life bicycle of strawberry plants begins either from seed or from runner plants, and continues until senescence. This post is an overview of the life of a strawberry institute from germination until withered, dark-brown leaves signify the passage from life unto decease.
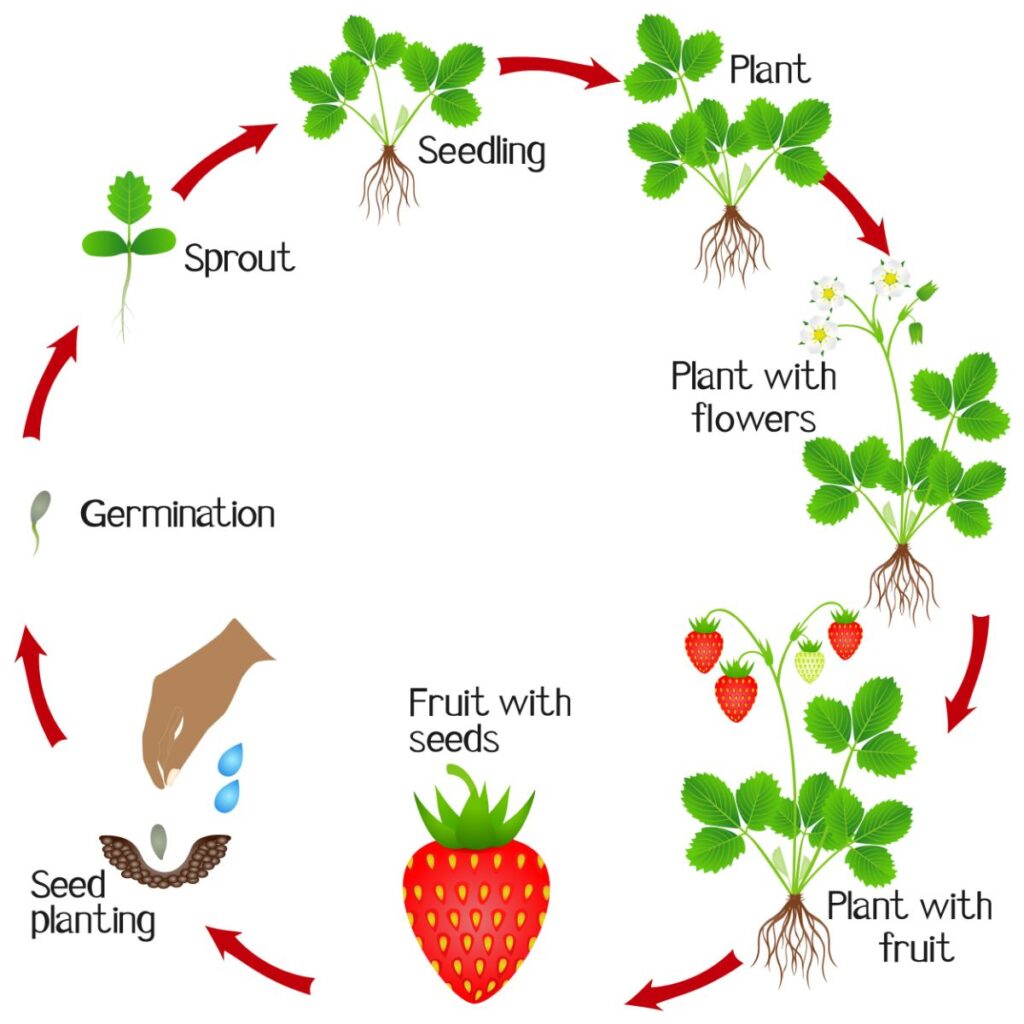
The Growth Cycle of Strawberry Plants
As with whatsoever cyclical scenario, it is hard to choose a starting signal (which came first, the chicken or the egg?). For the purposes of describing the life cycle of strawberry plants, a dual starting betoken will exist considered equally a sprouted strawberry seedling and a new strawberry runner. While both of these starting points require the existence of prior life, a give-and-take of the origins of life is outside the purview of this article.
Life Bicycle of Strawberries: Ancestry
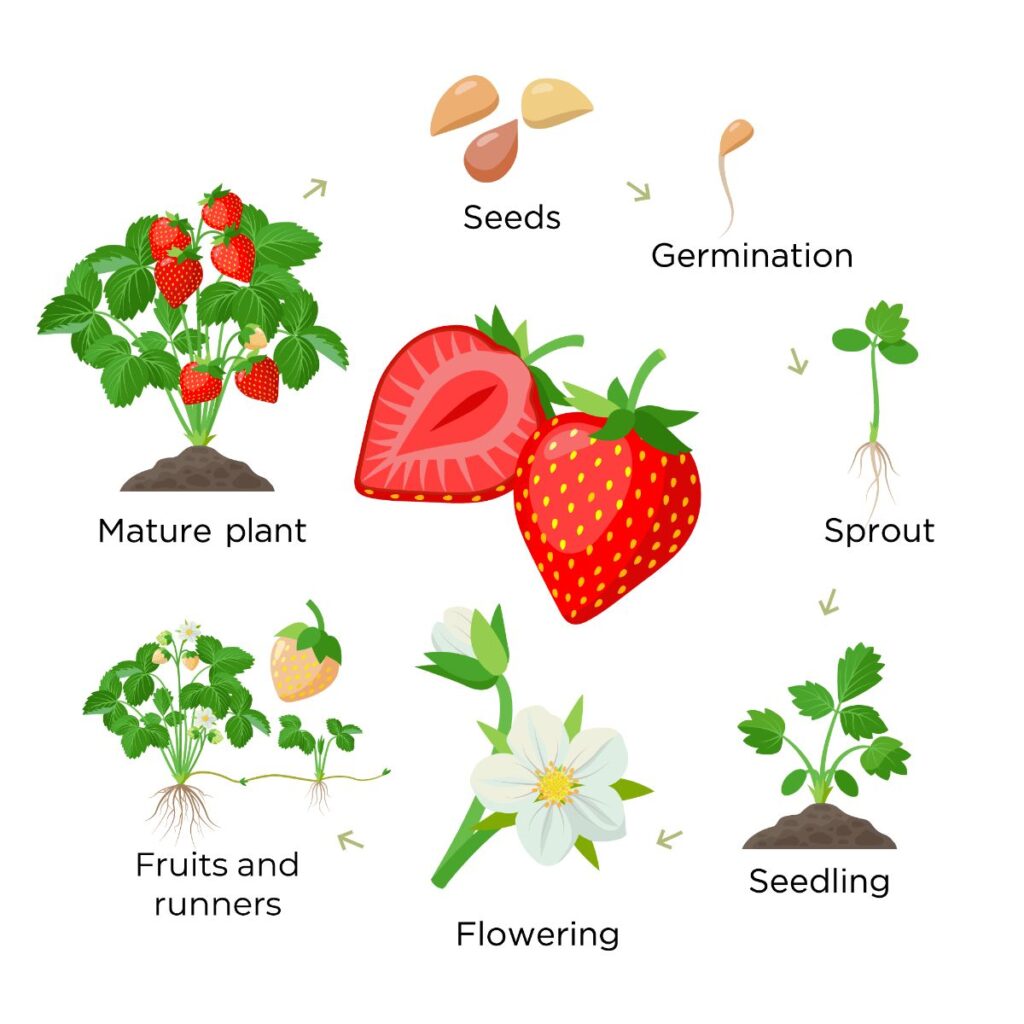
The strawberry seed, as with all seeds, contains the genetic material necessary for the continuation of the found species (see the Strawberry Seeds page for more details). Upon sprouting, the roots are sent downward into the soil, and the transformation of nutrients into constitute thing proceeds as the life cycle of the plant is perpetuated by resources obtained from the plants surroundings. These seedlings are genetically varied from the parent plants. Alternatively, established strawberry plants multiply themselves by means of clone or daughter plants extended from themselves by ways of stolons to root some distance away from the female parent found and be established equally an contained, but genetically identical, strawberry plant (see this page for more details: Strawberry Runners). Strawberry seeds will commonly sprout in the late wintertime or bound after a menstruation of cold stratification during winter months (simply this isn't required for all strawberry varieties) while runner plants are more often than not established later in the spring through the fall during warmer temperatures.
Jump to:
- The Growth Wheel of Strawberry Plants
- Life Cycle of Strawberries: Beginnings
- Growth Bike of Strawberry Plants: Maturation
- Growth Cycle of Strawberries: Multiplication & Expansion
- Life Cycle of Strawberry Plants: Seeds
- Life Bike of Strawberries: Life Span
- How Strawberry Plant Reproduce Themselves
- Life Bike of Strawberry Plants: Conclusion
Growth Bike of Strawberry Plants: Maturation
Once root growth commences, establish growth begins in hostage for both seedlings and runner plants. This allows all parts of the strawberry plant to grow and mature. The runner plants accept a distinct advantage over seedlings. They commencement out larger and have a more fully formed support system providing the energy needed for development. Just, by the time late summer and early fall rolls around, both seedlings and runner plants are normally established. In the process of growing, the plants will have sent along roots and produced a awning of photosynthesizing tri-lobed leaflets sitting atop not-woody stems. Both roots and leaves extend from the hub of the strawberry constitute, the crown.
Growth Cycle of Strawberries: Multiplication & Expansion
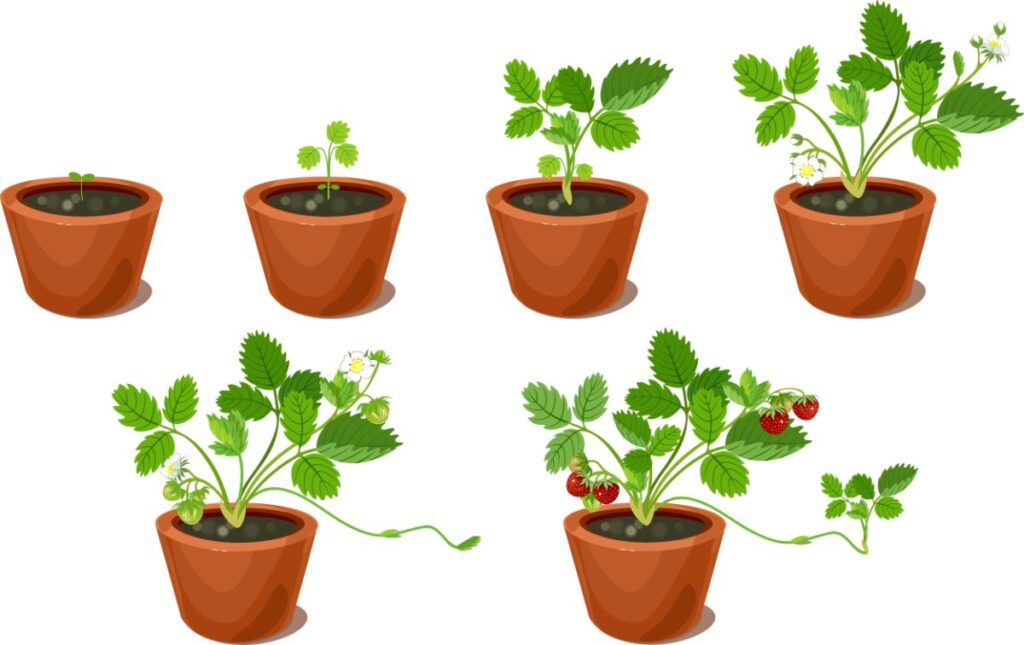

Once the plants have matured, they are ready to multiply and expand. They do this past means of the runner plants that accept already been mentioned. The runners (stolons) are usually betwixt 8 and 18 inches long, depending on the strawberry variety. These extensions serve to spread a strawberry found's range and observe areas more than favorable to growth, whether through higher soil quality or increased exposure to sunlight. Most strawberry varieties are practiced at multiplication in this fashion, and they are even considered an invasive weed in some situations.
Life Cycle of Strawberry Plants: Seeds
While strawberry plants produce runners, they don't put all their reproductive eggs in the same basket. Each strawberry plant devotes pregnant free energy to genetic diversification through seed production. Strawberry seeds come from strawberry flowers which come from strawberry buds which are formed in the crowns of established strawberry plants. In that location are some variances of flower bud, bloom, and strawberry production depending on which type of strawberry found is considered (encounter the Strawberry Variety page for more details). The well-nigh common of these types is the June-bearing strawberry, and it will exist considered here.
During the late summertime and early fall, strawberry plants begin forming flower buds inside their crowns. During this period, adequate water, lite, and nutrients are critical. The flower buds grade prior to winter and then move into dormancy (along with the rest of the found) as the temperature drops. When temperatures again warm in late winter or early on spring, the plants revive and immediately begin the transformation of the flower buds into flowers sitting atop stalks. These flowers, like virtually flowers, are so pollinated by insects and other pollinators. The consequence of pollination is a large mass of (usually red) accessory tissue studded with individual seed-containing fruits (in that location are also white strawberries, however). These achenes are attractive to birds and other creatures (including humans!) and are eaten. They are then digested. The remains, including many viable seeds, are and so deposited in unlike locations to sprout and begin the life cycle of strawberry plants once more.
Life Cycle of Strawberries: Life Bridge
The life arc of strawberries begins with the establishment of a new plant, peaks two to three years later, and then proceeds toward senescence and expiry 2 to three years following its height. Under platonic conditions, a strawberry plant can live up to five-6 years. After 3 productive years, however, they usually brainstorm to lose vigor, and the production of strawberries begins to decline rapidly. Eventually, as age progresses and the strawberry establish weakens, strawberries commonly succumb to ubiquitous opportunistic fungi or other environmental pathogens. The decease process usually commences with spots, defects, and browning of previously healthy plant tissues and ends with a dark-brown, withered, decomposing mass.
How Strawberry Found Reproduce Themselves

Strawberry plants are perennials. They tin reproduce by seed. Home gardeners find growing strawberry plants from seed notoriously hard.
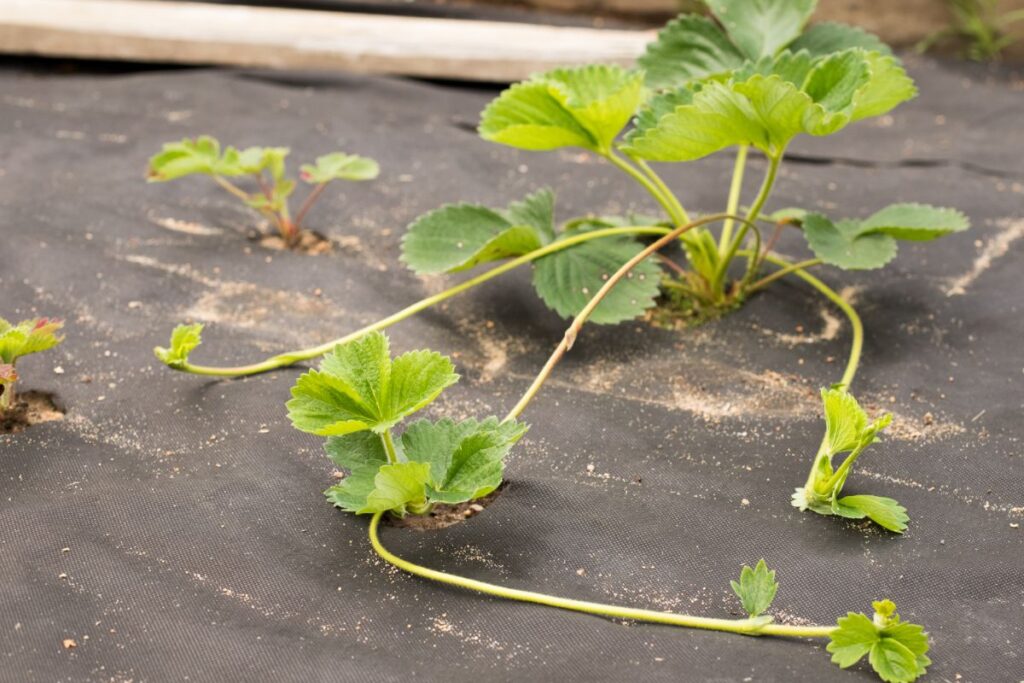
Strawberry plants too grow by runners. Runners are long stems with leaves that can develop their ain root arrangement where they touch moist soil.
A runner is the aforementioned plant equally its parent until it is no longer connected to the crown, the central mass of roots of the strawberry plant. But even later the runner is cutting off and transplanted somewhere else, information technology remains a clone of the mother plant. It is just a younger version of the strawberry plant you have been growing for one, two, iii, or more years.
Strawberry plants grow runners late in the season.
Strawberry plants don't put their energy into producing runners until after they have produced fruit. Later on the constitute has produced strawberries with their tiny seeds and as summertime days begin to wane, a strawberry found senses it is fourth dimension to put out runners.
There is a beginning and an end to "runner season" for strawberry plants. Summertime-begetting strawberry plants put all of their energy into producing fruit every bit the days are getting longer. Strawberries are coated with tiny seeds that can reproduce the institute, and, in nature, scarlet, sweet strawberries encourage animals to spread strawberry seeds far and wide.
After producing fruit, the constitute devotes its energy into producing runners. Long days trigger the production of a hormone called gibberellin that causes stems to grow longer. (You tin buy gibberellin to force strawberry plants to abound long stems, merely you don't need to, because the strawberry plants will do this on their own.) After producing fruit, the plant's energy is focused on making runners.
Scientists have discovered that the strawberry institute has to end producing its runners before temperatures boilerplate about 10 degrees Celsius (52 degrees Fahrenheit). Cool and cold weather cause the found to go dormant. Dormant strawberry plants take to survive on stored energy through the wintertime until next spring.
Life Wheel of Strawberry Plants: Conclusion
Throughout their life, strawberry plants provide many times their own weight in harvested strawberries. They are one of the most productive plants when what is produced from the weight of the institute is considered. Strawberries begin to ripen iv to 5 weeks subsequently the beginning flowers open up and continue to ripen for about three weeks. Accept you considered growing strawberries yourself this year? If and then, there are a host of suppliers from which you can detect multiple strawberry varieties for auction. Only see this directory: Strawberry Plants for Sale.
Understanding the growth cycle of strawberry plants can assistance yous in your strawberry growing endeavors. Good luck!
Source: https://strawberryplants.org/life-cycle-of-strawberry-plants/
0 Response to "How Long Til My Paphedelium Blooms Again"
إرسال تعليق